Vans / Engine-Sensors
Advertising
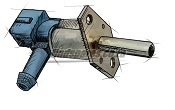
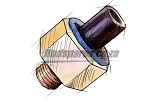
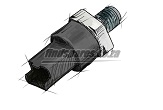
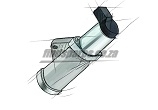
Principle work of the engine sensors
Electronic ECU control systems for vehicles use sensors that monitor engine performance and submit the information to a computer. Sensors in the internal combustion engine give information about the temperature of the engine coolant, the level or amount of motor oil, and record the exhaust gas stream.
Another sensor is the car's air intake sensor. This sensor is located in the piping system after the air filter. The pressure sensor is usually located in the intake manifold. This sensor measures the volume of air from the engine to the exhaust system. The pressure sensor is a silicon chip.
When manifold pressure changes, the silicon chip has the ability to flex. Engine speed sensors, pressure sensors and air intake sensors allows the ECU to calculate the base operating load of the internal combustion engine.
A water temperature sensor is usually located near the coolant outlet of the cylinder head. Water temperature sensors are necessary because the burning of fuel is less efficient when the engine is cold. When the internal combustion engine is cold, friction of the parts is greater and increases operational load.
Reports made by the water temperature sensor are used by the ECU to determine how much fuel enrichment is necessary. With this information, it makes necessary adjustments to improve the performance of cold engines. Gas sensors are usually located on the accelerator throttle. This sensor can also be mounted in the engine, but it depends on the type of engine and vehicle model.
Another sensor measures the ratio of the exhaust and is mounted in the exhaust system. This sensor supplies information needed for mixing fuel with air and, if necessary, make appropriate adjustments. Through our sites search engine of auto parts, you can easily find and purchase each sensor for petrol or diesel engines.