Cars / Electrical
Quotes
Electric vehicle system
Today's electrical systems in automobiles are increasingly complex and underline the limits of current technology, but they continue to be identical to the basic principles of 30 years ago. Part of the vehicle's electrical system is the battery. This device is used to store the current needed to start the engine and operate electrical accessories in the vehicle.
With an electrical system of 12 volts, Battery life is over 3 to 5 years depending on weather conditions. Another part of the vehicle's electrical system is the dynamo that produces electricity used by electrical appliances. Dynamo is driven by motor through belts and produces alternating AC current, which is converted to 12 volt DC-DC by a diode bridge (rectifier).
AC can not be stored, but is much more effective. Most dynamos (alternators) now use internal voltage regulators to maintain proper system voltage of 12.6-14.5 volts. The other major electrical component in the electrical system of the car is only used a few times a day, but is the largest energy consumer and the most critical to the performance of your car - it's the starter.
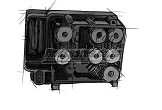
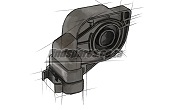
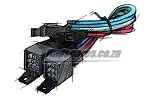
A DC starter turns the engine crankshaft via the flywheel to start the combustion process by creating compression in the cylinders. Voltage (current) of the starter is supplied directly from the battery and is controlled by a relay controlled by the ignition of the car. Some other parts included in the vehicle's electrical system are: sensors, electric motors, electric blades, switches, central mechanisms, electric pumps, rheostat, stepper motor, fuses and many other items.
Left Front